
This tutorial led you to learn the fundamentals of Angular and TypeScript.
TABLE OF CONTENT
- =>Introduction
- What is Angular?
- Why do we need Angular?
- Architecture and Building Blocks of Angular Apps
- Setting Up the Development Environment
- Your First Angular App
- Structure of Angular Projects
- Webpack
- TypeScript Fundamentals
- What is TypeScript?
- Creating First TypeScript Program
- Declaring Variables
- Types
- Type Assertions
- Arrow Functions
- Interfaces
- Classes
- Objects
- Constructors
- Access Modifiers
- Access Modifiers in Constructor Parameters
- Properties
- Modules
- Angular Fundamentals
- Creating Components
- Generating Components Using Angular CLI
- Templates
- Directives
- Services
- Dependency Injection
- Generating Services Using Angular CLI
- Exercise
Introduction
What is Angular?
Angular is a JavaScript framework for building client-side applications using HTML, CSS, and a programming language such as JavaScript. It is an open-source front-end web application platform based on TypeScript.

Before start using something new framework; everybody has lots of questions in his mind that What is it and Where does it fit in requirement? At which place it benefits and Why to use if there are lots of JavaScript frameworks out there.
Why do we need Angular? Why to use Angular and not some other JavaScript framework?

Angular makes HTML more expressive. It powers up HTML with language related features such as local variables, for loops, and if conditions.

Angular has powerful data binding. Application can easily display fields from data model, track changes, and process updates from the user so fast. It is built for providing speed. It has faster initial loads, faster change detections, and improved rendering times than other JavaScript frameworks.

Angular encourages modularity in application by design. It led us to create Applications as a set of building blocks, making it easier to create and reuse content. There most of the application build with JavaScript/ jQuery but as far the application gets more complex it is not easy to maintain the JavaScript and jQuery code.
It requires to properly structure the application. There are some JavaScript patterns out there e.g. Revealing Module Pattern, Prototype Pattern but these are must easy to lots beginners for JavaScript.
Angular has built-in support for making communication with a backend service. This makes it easy for web applications to integrate with a back-end service. It is preloaded with set to features to get and post data or execute server-side business logic.
Easily Testable

Picture credit from..
There are most the applications build with JavaScript or jQuery. Over the years various frameworks are build and evolved to make web applications development easier. Angular makes applications with clean structure that easy to understand and easy to maintain loosely coupled code. It makes applications more testable to write automated test to test the various part of the application.
Architecture and Building Blocks of Angular Apps
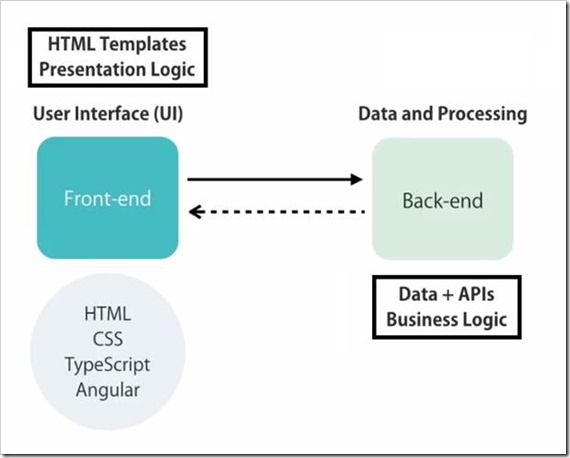
In modern web application, there are at least two parts a Front-end and Back-end. The Front-end is called client, it is the part of the web browser that user sees and interacts with. It includes user interface or UI for the application. It uses HTML, CSS, JavaScript/ TypeScript, Angular to create the Front-end. Front-end contains the HTML Templates and presentation logic to display the data and responding to the user e.g. navigation, listing data.
The Back-end consist of web servers or cloud which responsible for storing the data and doing any kind of processing. Back-end may one or more databases and APIs to make the data available to the client. For a large enterprise level application, it may also implement the business logic of the application like calculating the tax, shipping on various parameters
The Front-end or Client app talks to the Backend-end to get or save the data. At Back-end we create one or multiple HTTP Services / API to make data available to the client. These HTTP Services/ APIs are endpoint that are accessible via HTTP protocol so we call them to through HTTP request to get or save the data.
If we talk about Angular Building Blocks At the heart of every Angular App, we have one or more components. Application developed with Angular is comprised of a set of components and services which facilitates operations/functionality across those angular components.
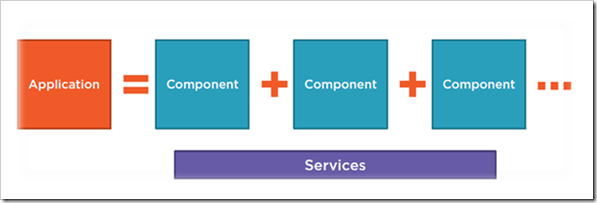
Angular component

Angular component is comprised of a template which is the HTML for the user interface fragment defining a view for the application. component encapsulates the Data, HTML mark-up and logic for a view.
Along this, a class for the code associated with the view. The class contains the data or properties for use in the view and methods, which perform actions button for the associated view e.g. responding to a button click.

Metadata
A component also has metadata, which provides additional information about the component to Angular. It is this metadata that identifies the class as an Angular component.
Modules
Every Angular application has at least one Angular module which called the application's root Angular module. As Application grows it can have any number of additional Angular modules including feature modules that consolidate the components for a specific application feature to make code maintainable. It is a container for groups of components.
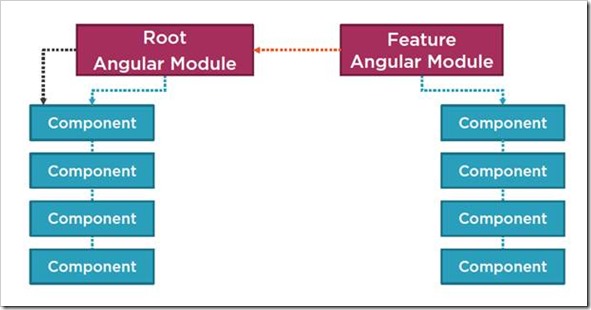
For an example, in real world scenario If we go to a grocery store then it has few shelf's to maintain their products/items to sell but in a big mall we found lots of I/0 to manage different categories of the products. Similarly, to maintain different type of components we can create multiple modules to organize the components.
If we see in Training web application, there are following modules can be created to manage the application:
Each module will manage their specific group of components, sub components to break the application in smaller and maintainable to facilitate a specific area of the application.
Conclusion:
In this section we have learned about the Angular and what/why Angular. Along this we have also tried to know the basic building blocks of the Angular to develop a web application
Next: Setting Up the Development Environment